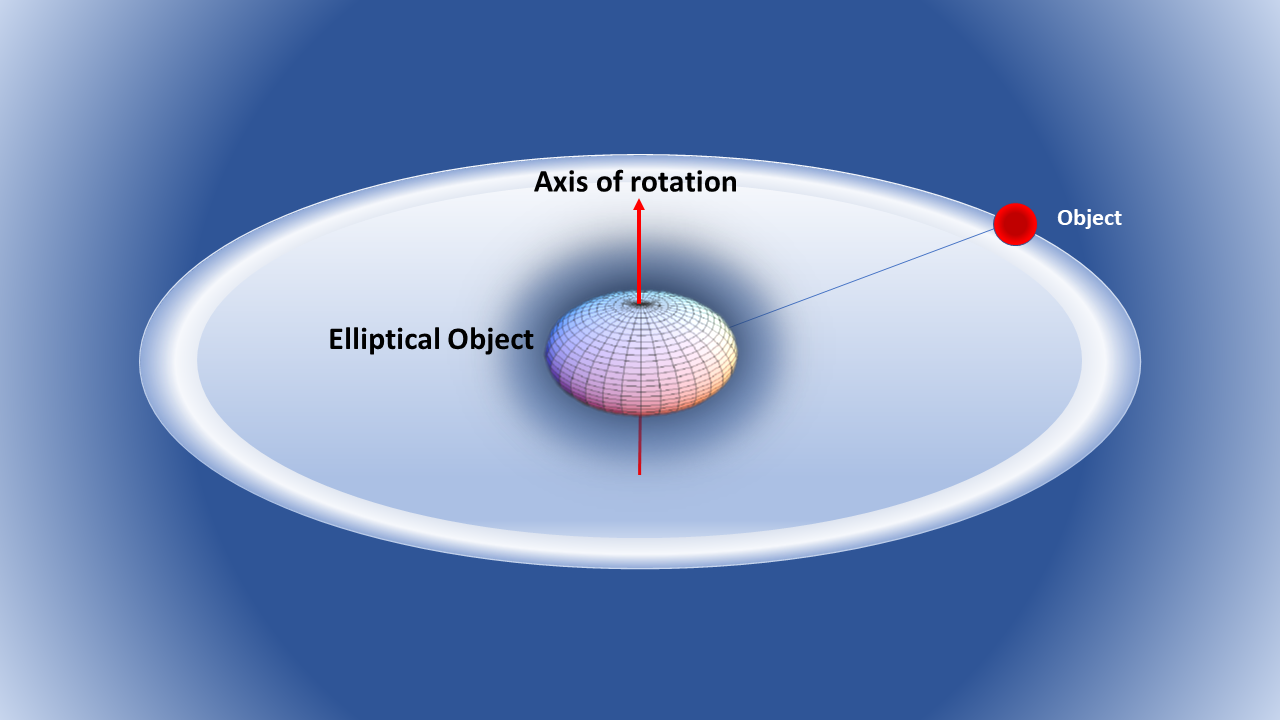
Lagrangian Solution of Schwarzschild-like Metric for an Elliptical Object
Astrophysics
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.55672/hij2022pp128-135Keywords:
Schwarzschild-like solution, Lagrangian solution, Spherical object, Elliptical objectsAbstract
The Lagrangian method was applied for a linearly transformed geodesic line element of a Schwarzschild-like solution instead of the tensor method. The solution shows that it is not only valid for spherical objects but also it is more comprehensive for elliptical celestial objects. Two types of kinetic and potential energy are the basis of the calculation. Hamiltonian and Lagrangian equality show that the problem has no potential energy. With this transformed geodesic line element, we obtained a new coefficient for the meridional advance of an experimental particle in Schwarzschild spacetime in terms of period, eccentricity, and mean distance. This new perigee equation is not only valid for the Schwarzschild metric (for a spherical object), but also more accurate for the Schwarzschild-like metric (for elliptical objects).
Downloads
References
[1] D. Dohrn and F. Guerra, "Geodesic correction to stochastic parallel displacement of tensors," in Stochastic Behavior in Classical and Quantum Hamiltonian Systems: Springer, 1979, pp. 241-249.
[2] H. Busemann, The geometry of geodesics. Courier Corporation, 2012.
[3] G. P. Paternain, Geodesic flows: Springer Science & Business Media, 2012. [Online]. Available.
[4] M. Balasubramanian, J. R. Polimeni, E. L. J. I. t. o. p. a. Schwartz, and m. intelligence, "Exact geodesics and shortest paths on polyhedral surfaces," vol. 31, no. 6, pp. 1006-1016
[5] D. R. Cheng and X. J. T. o. t. A. M. S. Zhou, "Existence of curves with constant geodesic curvature in a Riemannian 2-sphere," vol. 374, no. 12, pp. 9007-9028
[6] A. Fomenko and E. Kantonistova, "Topological classification of geodesic flows on revolution 2-surfaces with potential," in Continuous and Distributed Systems II: Springer, 2015, pp. 11-27.
[7] H. J. a. e.-p. Efrén Guerrero Mora, "Classification of geodesics on a cone in space," p. https://arxiv.org/pdf/2103.13531.pdf
[8] A. Kumar, R. Gangopadhyay, B. Tiwari, and H. M. Shah, "On Minimal Surfaces of Revolutions Immersed in Deformed Hyperbolic Kropina Space," Available: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2203.00220.pdf
[9] E. Hackmann and C. J. P. R. D. Lämmerzahl, "Geodesic equation in Schwarzschild-(anti-) de Sitter space-times: Analytical solutions and applications," vol. 78, no. 2, p. 024035Available: https://arxiv.org/pdf/1505.07973.pdf
[10] S. Chandrasekhar, "The mathematical theory of black holes," Research supported by NSF. Oxford/New York, Clarendon Press/Oxford University Press (International Series of Monographs on Physics. Volume 69), 1983, 663 p., vol. 1, 1983.
[11] G. J. F. d. P. P. o. P. Esposito, "Mathematical Structures of Space‐Time," vol. 40, no. 1, pp. 1-30Available: https://arxiv.org/pdf/gr-qc/9506088.pdf
[12] R. Almeida and D. F. J. L. i. M. P. Torres, "Generalized Euler–Lagrange equations for variational problems with scale derivatives," vol. 92, no. 3, pp. 221-229Available: https://arxiv.org/pdf/1003.3133.pdf
[13] C. Fox, An introduction to the calculus of variations. Dover Pubns, 1987.
[14] A. J. P. R. D. Schild, "Classical null strings," vol. 16, no. 6, p. 1722. doi: https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevD.16.1722
[15] T. Müller and J. J. E. j. o. p. Frauendiener, "Studying null and time-like geodesics in the classroom," vol. 32, no. 3, p. 747Available: https://arxiv.org/pdf/1105.0109.pdf
[16] U. J. G. R. Kostić and Gravitation, "Analytical time-like geodesics in Schwarzschild space-time," vol. 44, no. 4, pp. 1057-1072, 2012.
[17] E. Taillebois and A. J. P. R. A. Avelar, "Proper-time approach to localization," vol. 103, no. 6, p. 062223Available: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2009.13068.pdf
[18] H. Minkowski, "Die Grundgleichungen für die elektromagnetischen Vorgänge in bewegten Körpern," Mathematische Annalen, vol. 68, no. 4, pp. 472-525, 1910.
[19] Y. J. O. Kim and Spectroscopy, "Possible Minkowskian language in two-level systems," vol. 108, no. 2, pp. 297-300Available: https://arxiv.org/pdf/0811.0970.pdf
[20] N. M. J. Woodhouse, General relativity. Springer Verlag, 2007.
[21] B. Nikouravan, "Schwarzschild-like solution for ellipsoidal celestial objects," vol. 6, no. 6, pp. 1426-1430Available: https://ui.adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/2011IJPS....6.1426N/abstract
[22] B. Nikouravan and J. J. Rawal, "Mass as the Fifth Dimension of the Universe," vol. 2013. doi: DOI:10.4236/ijaa.2013.33030 Available: https://ui.adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/2003APS..APRR12005L/abstract
[23] M. Parry and E. Domina, "Field theory handbook, Including coordinate systems," ed: Springer–Verlac press, 1961.
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2022 Hyperscience International Journal

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.







 Google Scholar
Google Scholar  Crossref
Crossref  Scopus
Scopus  WorldCat
WorldCat  ORCID
ORCID  Scilit
Scilit  Mendeley
Mendeley  Internet Archive
Internet Archive